Activity Based Cost Drivers Examples
What's more, people waste their time arguing about the accuracy of cost-driver rates that are derived from individuals' subjective beliefs rather than addressing the. For example, the automated ABC model for Hendee Enterprises, a $12 million fabricator of awnings, took three days to calculate costs for its 40 departments,. Jul 28, 2010 - 8 min - Uploaded by MBAbullshitDotComClicked here and OMG wow!I'm SHOCKED how easy. Methods used for activity-based costing. Bill Evans Portrait In Jazz Rar Zip Opener. Activity-based costing requires accountants to use the following four steps: Identify the activities that consume resources and assign costs to those activities. Purchasing materials would be an activity, for example. Identify the cost drivers associated with each activity. A cost driver is an.
What is an 'Activity Cost Driver' An activity cost driver is a factor that influences or contributes to the expense of certain business operations. In activity-based costing (ABC), an activity cost driver drives the, maintenance or other variable expenses. Cost drivers are essential in, a branch of managerial accounting that allows managers to determine the costs to perform an activity at various activity levels. BREAKING DOWN 'Activity Cost Driver' A cost driver is an activity that is the root cause of why a cost occurs. It must be applicable and relevant to the event that is incurring a cost.
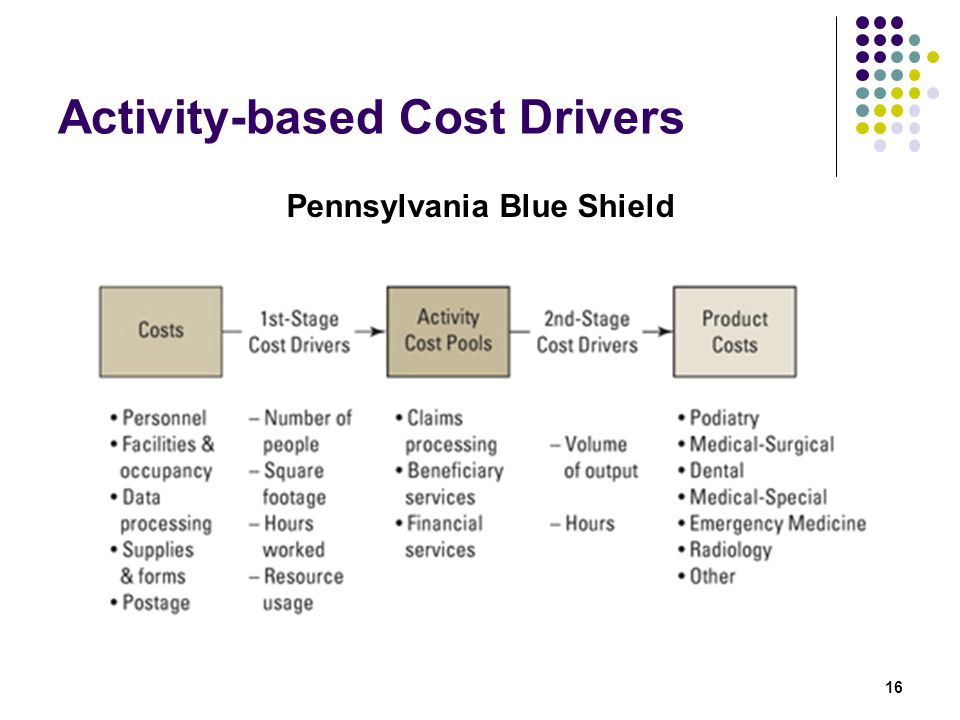

Download Mario And Sonic At The Olympic Games Iso Free. There may be multiple cost drivers responsible for the occurrence of a single expense. A cost driver assists with allocation expenses in a systematic manner that theoretically results in more accurate calculations of the true costs of a producing specific products. Examples of Cost Drivers The most common cost driver has historically been direct labor hours. Expenses incurred relating to the layout or structure of a building or warehouse may utilize a cost driver of square footage to allocate expenses.
More technical cost drivers include machine hours, the number of change orders, the number of customer contacts, the number of product returns, the machine setups required for production or the number of inspections. Example of Cost Allocation A factory has a machine that requires periodic maintenance. This maintenance incurs costs to be allocated to the products produced by the machinery. Therefore, the cost driver is identified and used as a base to distribute the costs.



